- Published on
ESLint 概念及原理探索:JavaScript 代码质量工具
- Authors

- Name
- Shoukai Huang
目录
在探索使用 AI 工具进行 Next.js 开发的旅程中,我们不可避免地会与一个名为 ESLint 的术语频繁邂逅。无论是深入研究前端框架的文档,还是仔细阅读源码,ESLint 总是一个不可忽视的存在。因此,我决定将我的探索和理解整理成文,以便更好地掌握这一工具。本文将从基础概念和核心原理出发,带领读者浅入深出地理解 ESLint,旨在提供一个清晰的视角,帮助大家在前端开发中更加得心应手。
关键要点:
- ESLint 是什么及其在前端开发中的重要性
- 抽象语法树(AST)在代码分析中的应用
- ESLint 的核心组件:规则、插件和解析器
- 如何理解和自定义 ESLint 规则
- ESLint 的工作流程和实现原理
1. ESLint 基础研究
1.1 ESLint 背景知识
什么是 Lint?标记源代码中有疑义段落的工具
Lint 在计算机科学中,lint是一种工具程序的名称,它用来标记源代码中,某些可疑的、不具结构性(可能造成bug)的段落。它是一种静态程序分析工具,最早适用于C语言,在UNIX平台上开发出来。后来它成为通用术语,可用于描述在任何一种计算机程序语言中,用来标记源代码中有疑义段落的工具。
什么是 ESLint?
ESLint 是一个可配置的 JavaScript 检查器。它可以帮助你发现并修复 JavaScript 代码中的问题。问题可以指潜在的运行时漏洞、未使用最佳实践、风格问题等。
1.2 背景概念
抽象语法树(Abstract Syntax Tree,AST)
简称语法树(Syntax tree),是源代码语法结构的一种抽象表示。它以树状的形式表现编程语言的语法结构,树上的每个节点都表示源代码中的一种结构。之所以说语法是“抽象”的,是因为这里的语法并不会表示出真实语法中出现的每个细节。
通过 astexplorer.net 得到形象理解:JavaScript 代码如下
/**
* Paste or drop some JavaScript here and explore
* the syntax tree created by chosen parser.
* You can use all the cool new features from ES6
* and even more. Enjoy!
*/
let size = 10;
if (size > 5) {
console.log("size is greater than 5");
}
右侧得到的 AST 结构
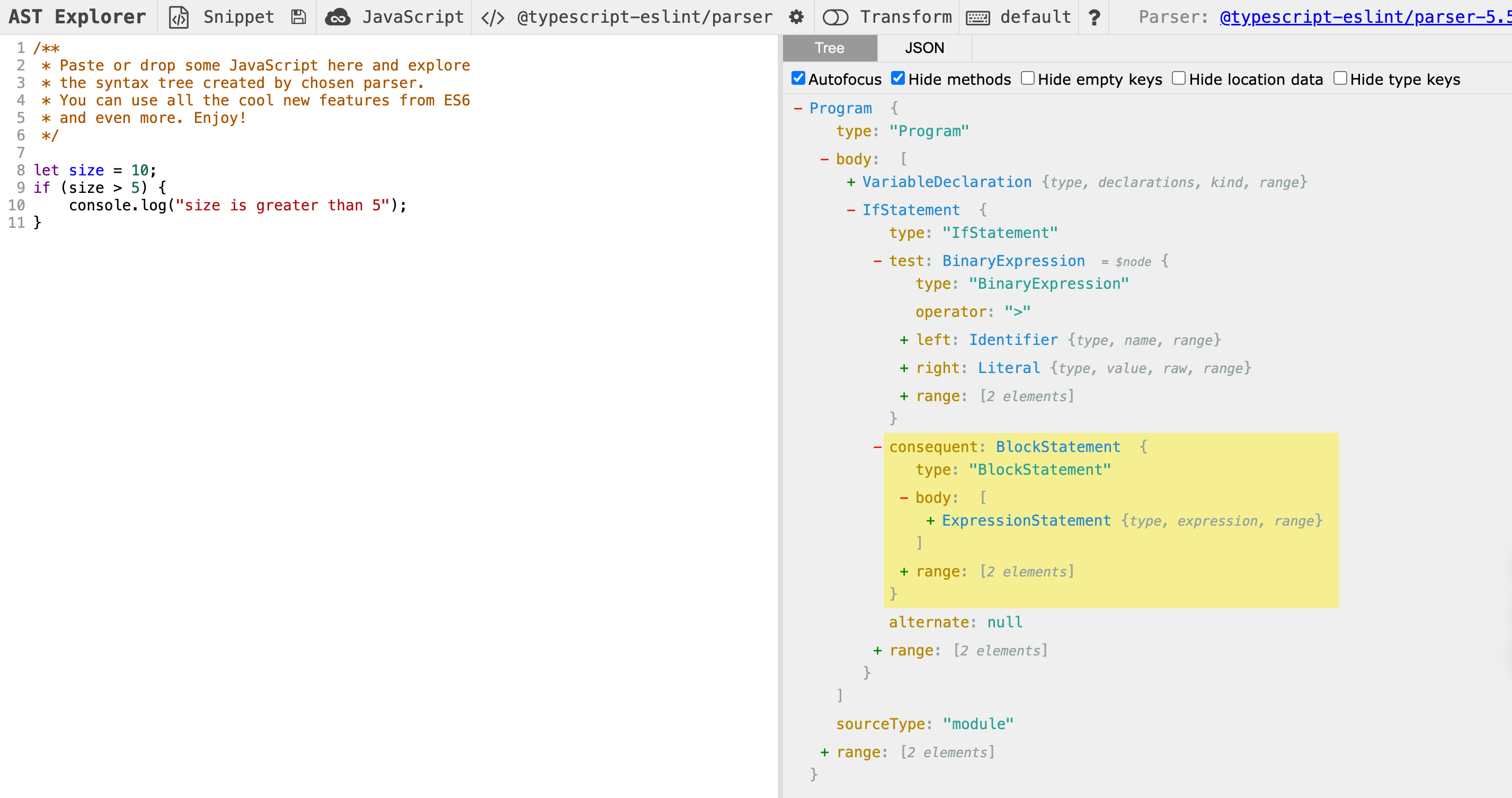
代码转换:支持使用 Transform 插件来转换代码,用户可以添加或修改 Prettier 参数来观察代码如何被转换。
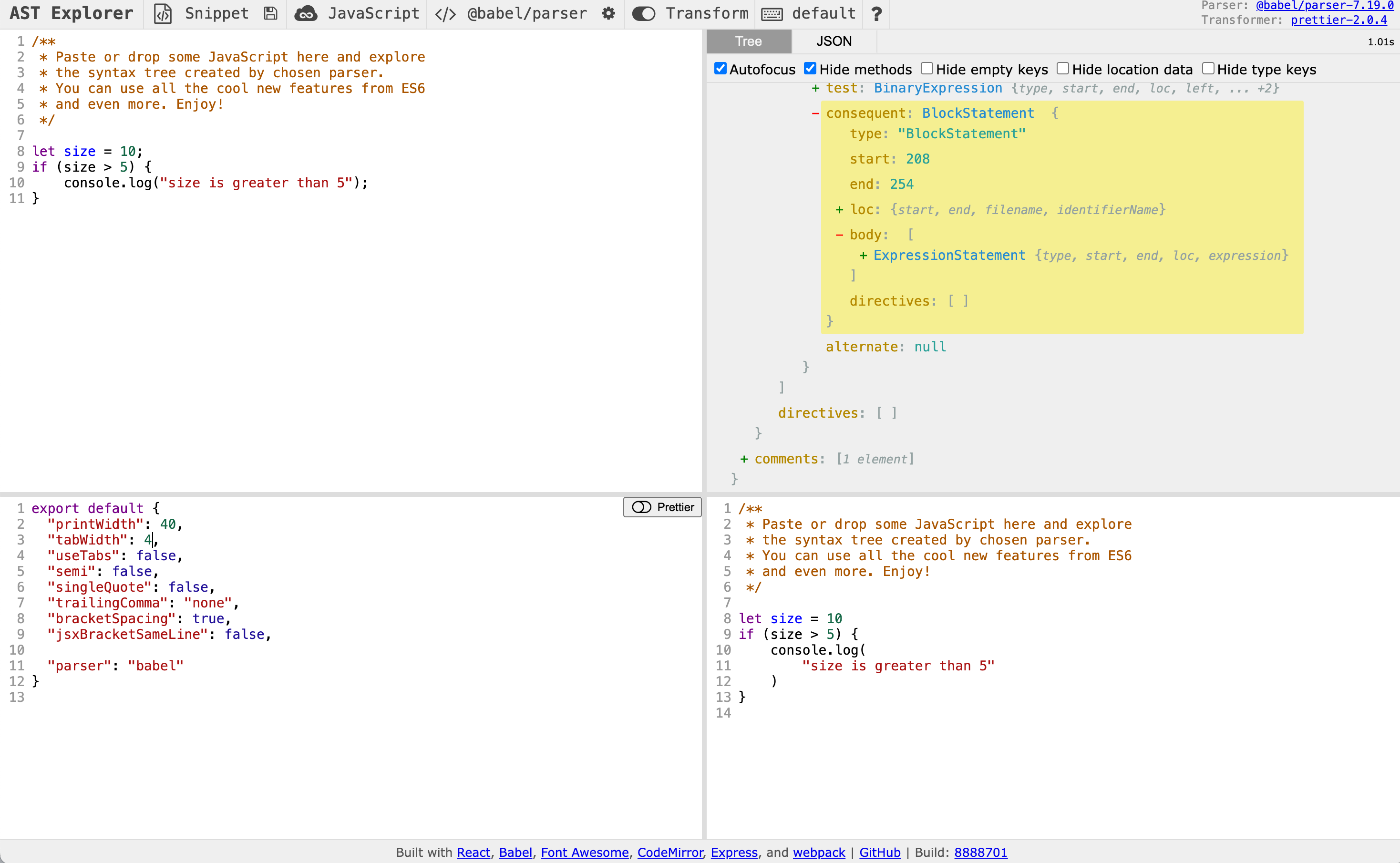
注意:里面 IfStatement 后在后面代码里提到;
Espree 解析器
Espree 最初是 Esprima v1.2.2 的一个分支,这是 Esprima 在 ECMAScript 6 开始工作之前的最后一个稳定发布的版本。Espree 现在构建在 Acorn 之上,Acorn 具有允许扩展核心功能的模块化架构。Espree 的目标是生成类似于具有类似 API 的 Esprima 的输出,以便可以使用它来代替 Esprima。
Espree started out as a fork of Esprima v1.2.2, the last stable published released of Esprima before work on ECMAScript 6 began. Espree is now built on top of Acorn, which has a modular architecture that allows extension of core functionality. The goal of Espree is to produce output that is similar to Esprima with a similar API so that it can be used in place of Esprima.
Espree 是 ESLint 项目使用的 JavaScript 解析器。Espree 的目标是生成与 Esprima 类似的抽象语法树(AST)和 API,以便它可以作为 Esprima 的替代品使用。
通过 astexplorer.net 使用 Espree 得到 Esprima 抽象语言 AST;
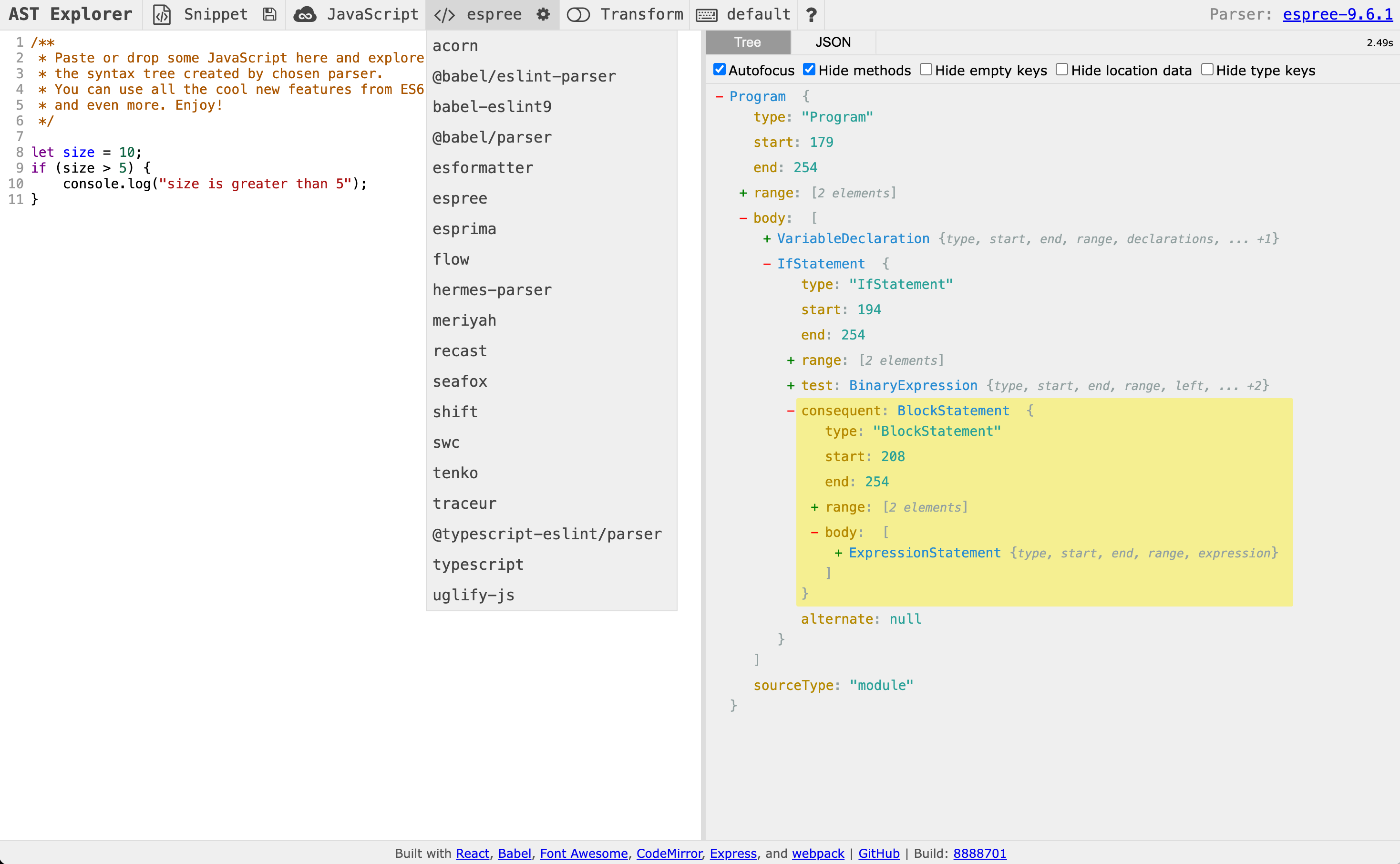
2. ESLint 理论学习
2.1 相关概念
规则
规则是 ESLint 的核心构建块。规则会验证你的代码是否符合预期,以及如果不符合预期该怎么做。规则还可以包含针对该规则的额外配置项。ESLint 包括数百个可以使用的内置规则。此外你也可以创建自定义规则或使用别人用插件创建的规则。
在规则参考章节中,有 ESLint 的规则示例
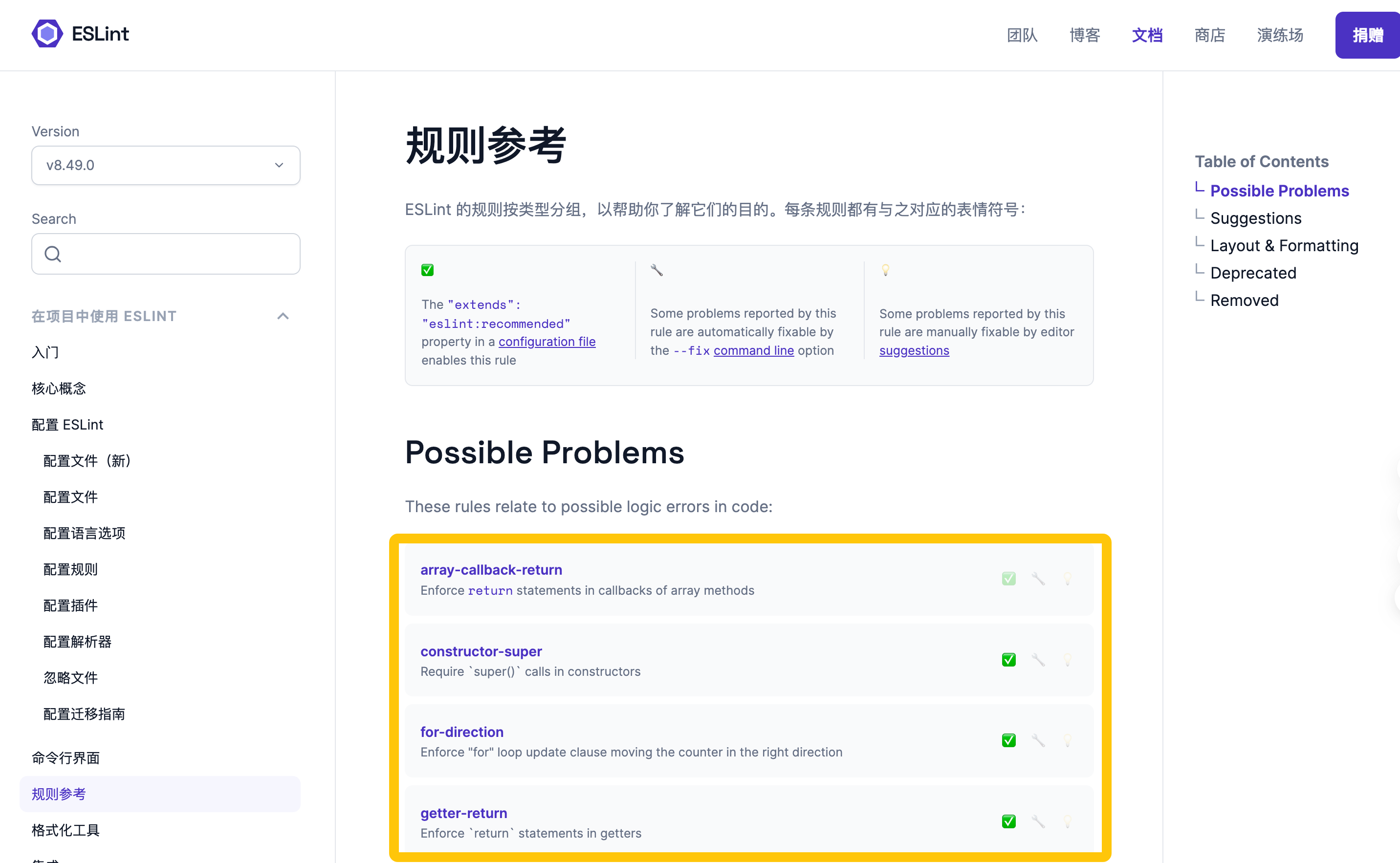
以 no-dupe-else-if 规则为例。链接:https://zh-hans.eslint.org/docs/latest/rules/no-dupe-else-if
展示正确和错误的规则说明
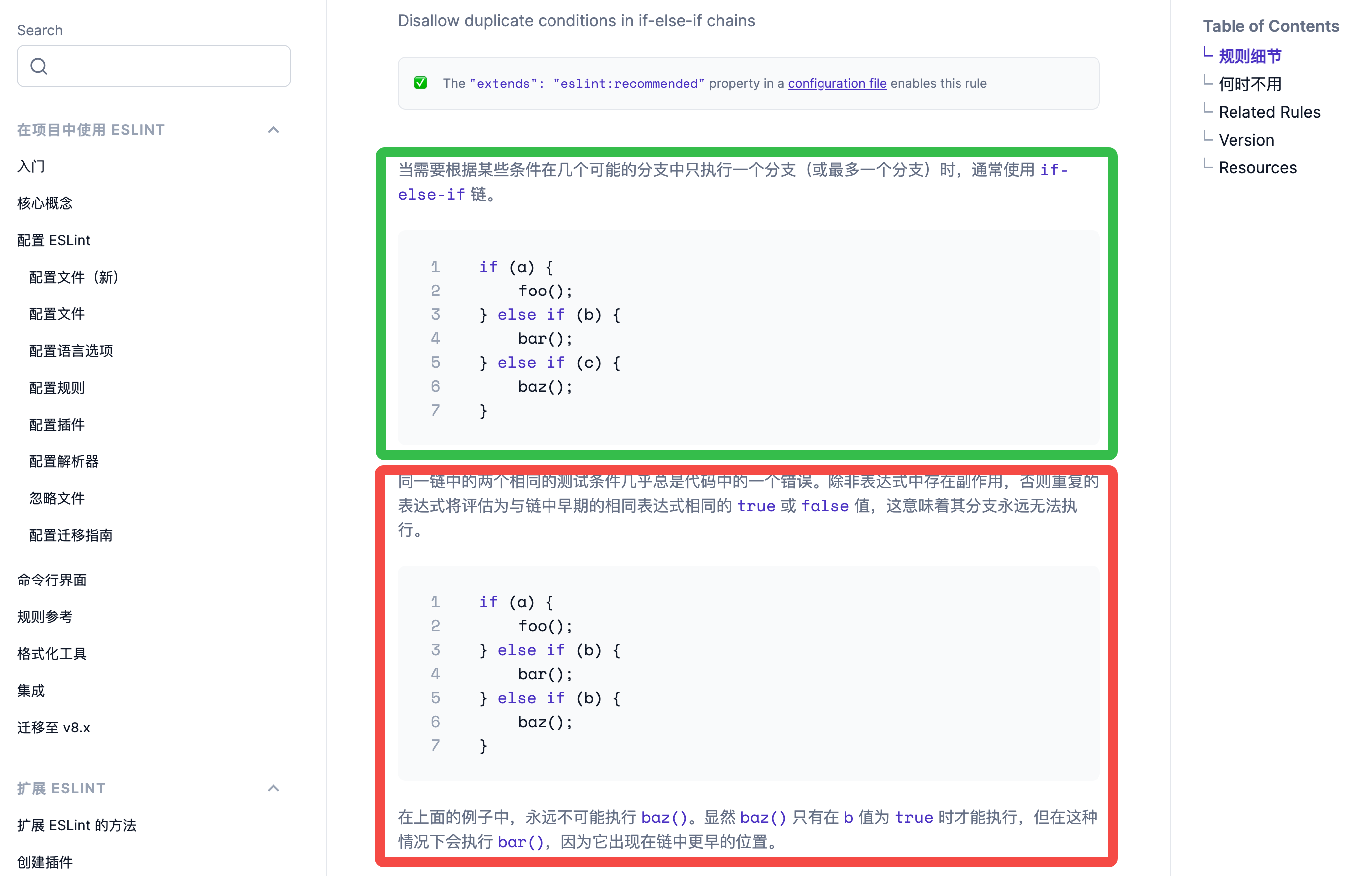
然后展示规则细节、Related Rules、代码及规则测试(单元测试)
代码较为短小精炼,
- 规则测试链接: no-dupe-else-if.js
- 规则源码链接: no-dupe-else-if.js
no-dupe-else-if.js 源码如下所示
/**
* @fileoverview Rule to disallow duplicate conditions in if-else-if chains
* @author Milos Djermanovic
*/
"use strict";
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Requirements
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
const astUtils = require("./utils/ast-utils");
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Helpers
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/**
* Determines whether the first given array is a subset of the second given array.
* @param {Function} comparator A function to compare two elements, should return `true` if they are equal.
* @param {Array} arrA The array to compare from.
* @param {Array} arrB The array to compare against.
* @returns {boolean} `true` if the array `arrA` is a subset of the array `arrB`.
*/
function isSubsetByComparator(comparator, arrA, arrB) {
return arrA.every(a => arrB.some(b => comparator(a, b)));
}
/**
* Splits the given node by the given logical operator.
* @param {string} operator Logical operator `||` or `&&`.
* @param {ASTNode} node The node to split.
* @returns {ASTNode[]} Array of conditions that makes the node when joined by the operator.
*/
function splitByLogicalOperator(operator, node) {
if (node.type === "LogicalExpression" && node.operator === operator) {
return [...splitByLogicalOperator(operator, node.left), ...splitByLogicalOperator(operator, node.right)];
}
return [node];
}
const splitByOr = splitByLogicalOperator.bind(null, "||");
const splitByAnd = splitByLogicalOperator.bind(null, "&&");
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Rule Definition
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/** @type {import('../shared/types').Rule} */
module.exports = {
meta: {
type: "problem",
docs: {
description: "Disallow duplicate conditions in if-else-if chains",
recommended: true,
url: "https://eslint.org/docs/latest/rules/no-dupe-else-if"
},
schema: [],
messages: {
unexpected: "This branch can never execute. Its condition is a duplicate or covered by previous conditions in the if-else-if chain."
}
},
create(context) {
const sourceCode = context.sourceCode;
/**
* Determines whether the two given nodes are considered to be equal. In particular, given that the nodes
* represent expressions in a boolean context, `||` and `&&` can be considered as commutative operators.
* @param {ASTNode} a First node.
* @param {ASTNode} b Second node.
* @returns {boolean} `true` if the nodes are considered to be equal.
*/
function equal(a, b) {
if (a.type !== b.type) {
return false;
}
if (
a.type === "LogicalExpression" &&
(a.operator === "||" || a.operator === "&&") &&
a.operator === b.operator
) {
return equal(a.left, b.left) && equal(a.right, b.right) ||
equal(a.left, b.right) && equal(a.right, b.left);
}
return astUtils.equalTokens(a, b, sourceCode);
}
const isSubset = isSubsetByComparator.bind(null, equal);
return {
IfStatement(node) {
const test = node.test,
conditionsToCheck = test.type === "LogicalExpression" && test.operator === "&&"
? [test, ...splitByAnd(test)]
: [test];
let current = node,
listToCheck = conditionsToCheck.map(c => splitByOr(c).map(splitByAnd));
while (current.parent && current.parent.type === "IfStatement" && current.parent.alternate === current) {
current = current.parent;
const currentOrOperands = splitByOr(current.test).map(splitByAnd);
listToCheck = listToCheck.map(orOperands => orOperands.filter(
orOperand => !currentOrOperands.some(currentOrOperand => isSubset(currentOrOperand, orOperand))
));
if (listToCheck.some(orOperands => orOperands.length === 0)) {
context.report({ node: test, messageId: "unexpected" });
break;
}
}
}
};
}
};
辅助函数
- isSubsetByComparator:
- 判断一个数组是否是另一个数组的子集。使用一个比较函数来比较两个元素是否相等。
- splitByLogicalOperator:
- 根据给定的逻辑运算符(
||或&&),将一个节点拆分成多个条件节点。如果节点是LogicalExpression并且运算符匹配,则递归拆分。
- 根据给定的逻辑运算符(
- splitByOr 和 splitByAnd:
- 分别是
splitByLogicalOperator的快捷方式,用于处理||和&&。
- 分别是
核心逻辑
- equal 函数:
- 判断两个节点是否相等。特别地,对于逻辑表达式,
||和&&被视为可交换的运算符。
- 判断两个节点是否相等。特别地,对于逻辑表达式,
- isSubset 函数:
- 使用
isSubsetByComparator和equal函数来判断一个条件是否是另一个条件的子集。
- 使用
- IfStatement 处理器:
- 处理
IfStatement节点,检查if-else-if链中是否有重复的条件。 - 如果发现重复条件,使用
context.report报告错误。
- 处理
处理流程
- 对于每个
IfStatement,提取测试条件,并根据逻辑运算符拆分成多个条件。 - 遍历
if-else-if链,检查当前条件是否被前一个条件覆盖。 - 如果发现重复或被覆盖的条件,报告错误。
里面的 IfStatement 前文提到过,是 AST 结构的一部分。
如何自定义规则,参考官网: https://zh-hans.eslint.org/docs/latest/extend/custom-rules
插件
ESLint 插件是一个包含 ESLint 规则、配置、解析器和环境变量的集合的 npm 模块。通常插件包括自定义规则。插件可以强制使用某个风格指南并支持 JavaScript 扩展(比如 TypeScript)、库(比如 React)和框架(比如 Angular)。
解析器
ESLint 解析器将代码转换为 ESLint 可以评估的抽象语法树(AST, abstract syntax tree)。默认情况下,ESLint 使用内置的与标准 JavaScript运行时和版本兼容的 Espree 解析器。
自定义解析器让 ESLint 可以解析非标准的 JavaScript 语法。通常自定义解析器会被包含在可共享配置或插件中,这样你就不需要直接使用它们了。
比如用于让 ESLint 可以解析 TypeScript 代码的 @typescript-eslint/parser 解析器就被包含在 typescript-eslint 项目中。
如何配置自定义解析器,参考官网:https://zh-hans.eslint.org/docs/latest/use/configure/parser
集成
ESLint 相关集成生态是使 ESLint 成为如此有用的工具的原因之一。例如,许多代码编辑器都有 ESLint 扩展,这让工作时,可以即刻在文件中查看相关的代码 ESLint 结果,这样你就不需要使用 ESLint 命令行来查看检查结果。
2.2 ESLint 实现原理
ESLint 实现原理涉及到几个核心概念,包括抽象语法树(AST)、规则(Rule)、插件(Plugin)以及发布订阅模式。
工作流程如下:
- ESLint 使用解析器(如:Espree)将 JavaScript 代码转换成 AST。
- ESLint 为每个规则创建一个上下文对象,并注册监听器。
- ESLint 遍历 AST,当遇到特定的节点时,触发相应的监听器。
- 监听器调用规则的处理函数,执行校验逻辑。
- 如果规则校验失败,ESLint 会收集错误信息,并在分析结束后报告。
通过这些机制,ESLint 能够高效地对 JavaScript 代码进行静态分析,帮助开发者发现和修复潜在的问题,提高代码质量和一致性。
3. ESLint 学习资源
3.1 参考资料
- Lint 工具介绍:Wikipedia - Lint
- ESLint 官方文档:ESLint 中文文档
- 抽象语法树详解:Wikipedia - 抽象语法树
- AST Explorer 在线工具:AST Explorer
- Espree 解析器:GitHub - espree